Have you ever wondered why you or others act the way they do? Perhaps you’ve taken a general personality quiz to determine your strengths and weaknesses, but they always seem to fall short, leaving you more confused than confident.
The good news is that the Enneagram can help you find the answers that you’re looking for. It is a system that divides people into 9 different personality types, each with unique traits, fears, and motivations. You can use it to better yourself both personally and professionally, and by that, I mean taking the necessary steps to accept and address your flaws while embracing your strengths.
Today, I make it easier to understand the Enneagram of Personality test by taking a closer look at this insightful system and how it provides an incredibly detailed framework for understanding who you are.
1. Introduction to the Enneagram Test
What is the Enneagram?
The Enneagram (pronounced ANY-a-gram) is a system that helps you understand your personality. It does this by dividing human behavior into nine different personality types based on your desires, insecurities, and self-awareness.
What makes this test so unique is its ability to showcase how different aspects of your personality influence the way you feel and think about yourself and your relationships with others. It’s a powerful resource you can use to achieve personal growth, adapt to change, and improve your emotional skills.
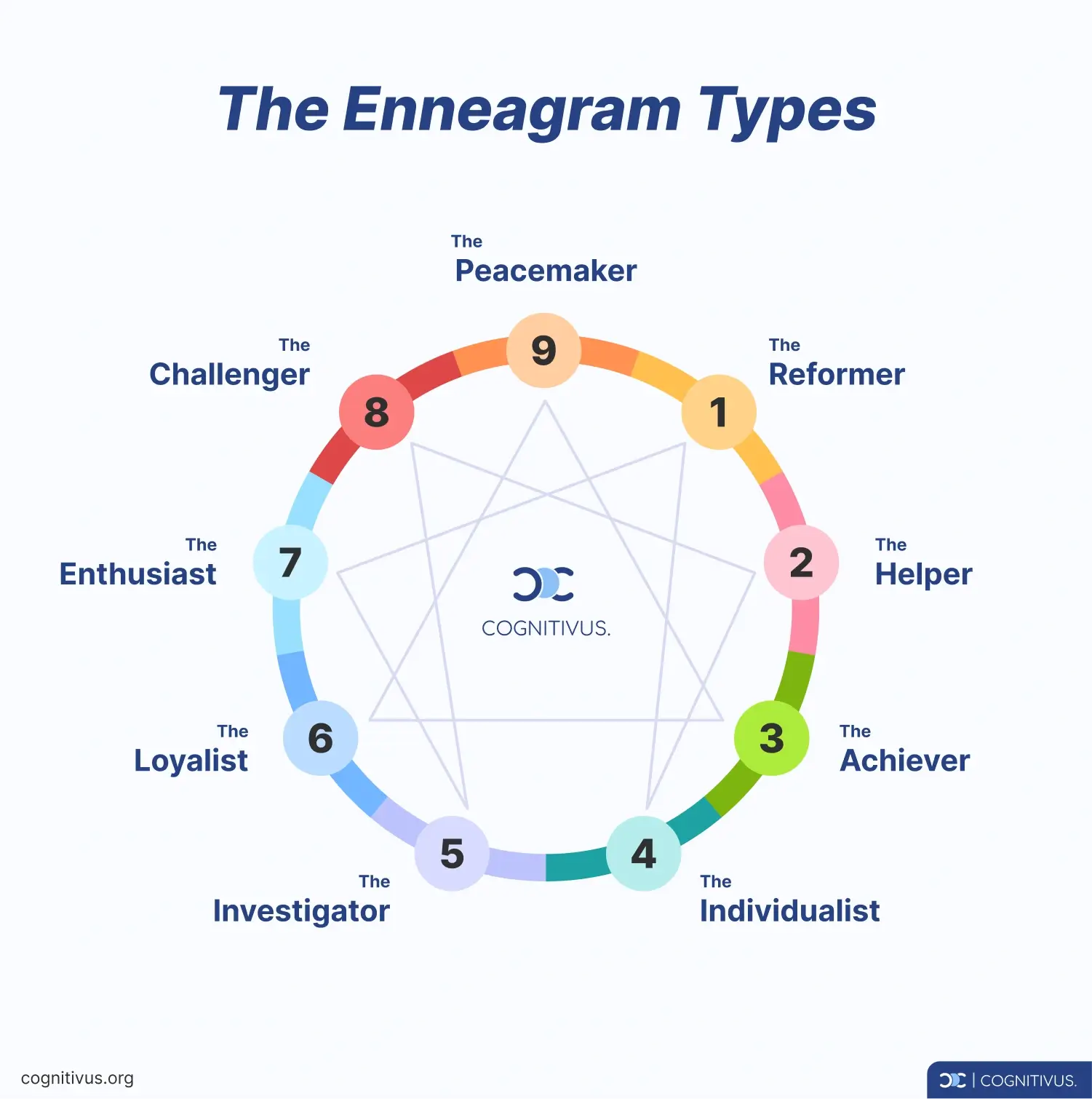
The Enneagram diagram
The Enneagram diagram is the symbol of this personality system, which consists of a circle surrounded by nine points. Each point represents a different personality type with its own traits, motivations, and ways of thinking, feeling, and behaving.
The lines in the diagram connecting each of the nine points show how each personality type is related to the others and how it’s possible for people to move between these types under different circumstances. So, for example, some personalities can either fall apart or grow when under stress. Don’t worry, we’ll go through this later in this article.
The story behind the Enneagram
Even though the Enneagram’s exact origins are unclear, we know that it has been linked to ancient Greek philosophy, Christian mysticism, and Sufi traditions.
It was around the mid-20th century when philosopher Oscar Ichazo and psychiatrist Claudio Naranjo introduced psychological insights that contributed to the Enneagram. Claudio Naranjo, a Chilean-born psychiatrist, lived and worked in the U.S. in the late 1960s, when he first heard of Oscar Ichazo from former patients who had experienced profound transformations under Ichazo's guidance. Intrigued, Naranjo met Ichazo and integrated his teachings, which combined ancient wisdom with modern psychology.
This collaboration led to a comprehensive system for personal growth and self-awareness that we know as the Enneagram, used by millions worldwide today.
What does Enneagram mean?
The term 'Enneagram' combines two Greek words: "ennea" (ἐννέα), meaning nine, and "grammos" (γράμος), meaning something written or drawn.
This name hints at the nine distinct points of the Enneagram symbol, each representing a different personality type.
Why take the Enneagram test?
Think of the Enneagram as an advanced personality test that brings clarity and insight. It helps you understand your motives and fears, which you can use to transform your relationships, cope with stress, and become a better leader in your professional life.
The test pushes you to confront the "whys" behind your actions by highlighting parts of your personality you might overlook. With this awareness, you can make more informed choices and live a more fulfilling life.
2. The 9 Enneagram Personality Types
As previously mentioned, the Enneagram has 9 dominant personality types. Each type has a different way of interacting with the world and understanding their behaviors and motivations.
Each type is characterized by a core fear, desire, and passion (also known as the deadly sin). The core fear represents the underlying anxiety that influences your behavior; the core desire is your primary motivation; and the core passion includes the emotional habits that distract you from your goals.
The nine types are grouped into three Enneagram triads based on primary emotional responses:
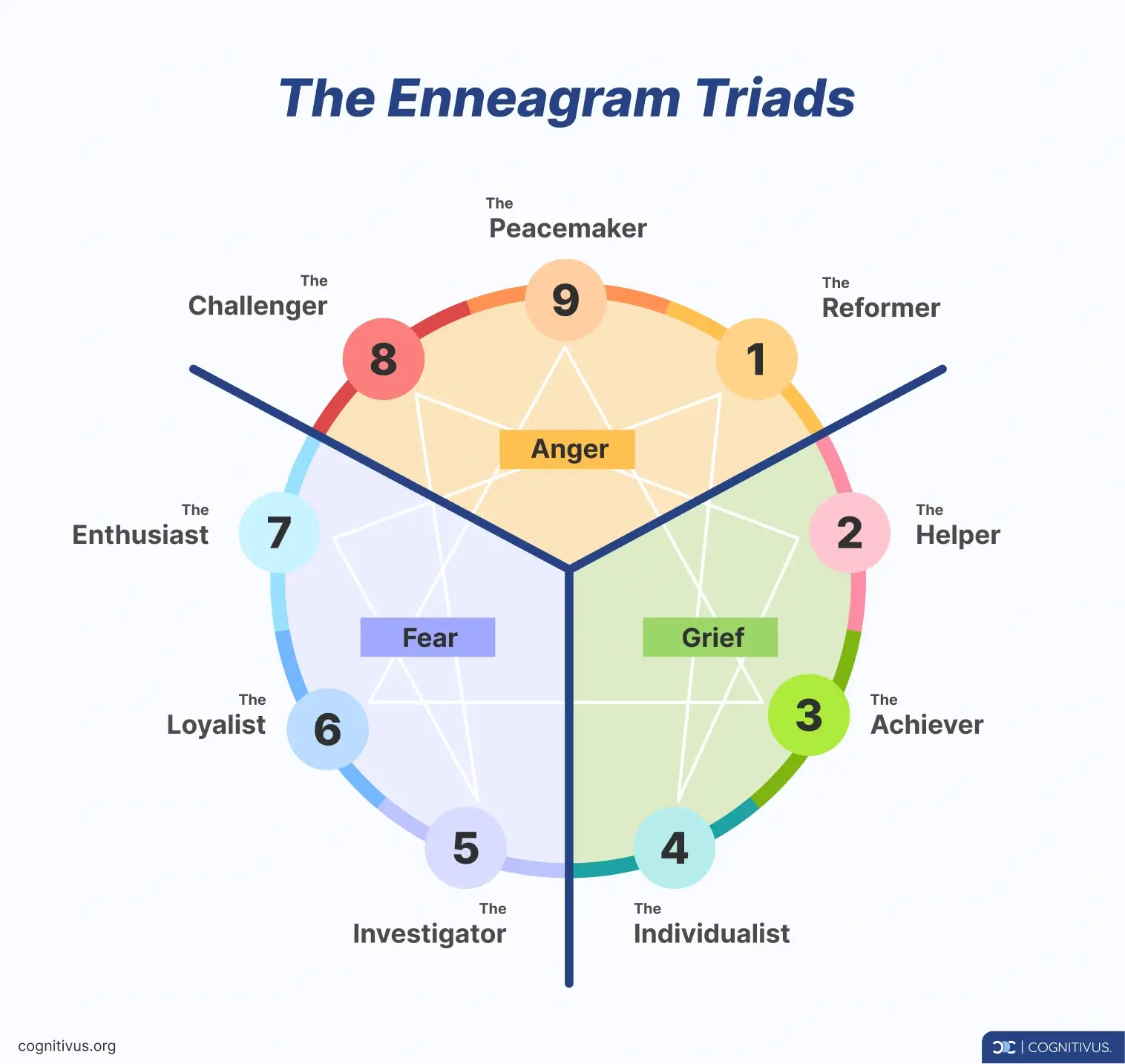
- The Anger Triad (Types 8, 9, and 1)
- The Grief Triad (Types 2, 3, and 4)
- The Fear Triad (Types 5, 6, and 7)
Each triad shares a common emotional struggle that shapes the way you think, feel, and behave.
Let’s take a look at the 9 Enneagram personality types in more detail below.

Type 1: The Reformer
Reformers (also called Perfectionists) strive for perfection and have a strong sense of right and wrong, always aiming to improve themselves and the world around them.
- Description: Principled, purposeful, self-controlled, and perfectionistic
- Core fear: Being bad, unbalanced, defective, or corrupt
- Core desire: To be good, have integrity, and be balanced
- Passion: Anger
When Type 1s slip into an unhealthy state, their pursuit of perfection becomes rigid and controlling. They believe their way is the only right way, pushing others to meet their impossibly high standards. This need for order and correctness can make them overly critical, leading to frustration when things don’t go perfectly, and straining relationships as they try to fix everything around them.
Type 2: The Helper
Enneagram type 2s are referred to as the “The Helpers” or “The Givers”. They find joy in serving others and seek to be loved and appreciated, often putting others' needs before their own.
- Description: Generous, demonstrative, people-pleasing, and possessive
- Core fear: Being unloved and unwanted for themselves alone
- Core desire: To feel loved
- Passion: Pride
For Type 2s, an unhealthy state emerges when their desire to help is no longer genuine. Instead of truly caring for others, they seek love and validation through their acts of kindness. This turns into manipulation, as they help only to feel appreciated. They may become overbearing, neglecting their own needs and feeling resentful when they don’t get the recognition they desperately seek.
Type 3: The Achiever
Achievers are goal-oriented, constantly seeking success and validation, and driven by a need to be admired and to stand out.
- Description: Adaptive, excelling, driven, and image-conscious
- Core fear: Being worthless or without inherent value
- Core desire: To feel valuable and worthwhile
- Passion: Deceit
If Type 3s don't receive the validation they seek, they can enter an unhealthy state. As unhealthy type 3s, they become overly competitive, deceitful, and obsessed with their image, neglecting their true self. They may manipulate situations to maintain the appearance of success, leading to burnout, superficial relationships, and a loss of genuine self-worth.
Type 4: The Individualist
Enneagram Type 4s are deeply introspective and yearn to express their unique identity, often feeling different or special compared to others.
- Description: Expressive, dramatic, self-absorbed, and temperamental
- Core fear: Having no identity or significance
- Core desire: To find themselves and their significance
- Passion: Envy
Type 5: The Investigator
They crave knowledge and seek to understand the world through analysis, valuing privacy and independence.
- Description: Perceptive, innovative, secretive, and isolated
- Core fear: Being helpless, useless, or incapable
- Core desire: To be competent
- Passion: Avarice
Type 6: The Loyalist
They value security and loyalty, often preparing for potential risks and seeking guidance from trusted authorities.
- Description: Engaging, responsible, anxious, and suspicious
- Core fear: Being without support or guidance
- Core desire: To have security and support
- Passion: Fear
Type 7: The Enthusiast
Enthusiasts are adventure seekers who love to explore new experiences and possibilities, constantly looking for excitement and fun.
- Description: Spontaneous, versatile, acquisitive, and scattered
- Core fear: Being deprived or in pain
- Core desire: To be satisfied and content
- Passion: Gluttony
Type 8: The Challenger
This personality type is described as that of natural leaders who assert control and seek to protect themselves and others, often taking charge.
- Description: Self-confident, decisive, willful, and confrontational
- Core fear: Being harmed or controlled by others
- Core desire: To protect themselves and be in control of their own life
- Passion: Lust
Type 9: The Peacemaker
Peacemakers strive for inner and outer peace, often avoiding conflict, to maintain harmony and create a sense of calm.
- Description: Receptive, reassuring, complacent, and resigned
- Core fear: Loss of connection and fragmentation
- Core desire: To have inner stability and peace of mind
- Passion: Sloth
3. Enneagram Wings, Levels & Arrows
While the Enneagram does a great job of categorizing your personality, it also describes your accompanying traits, painting a clearer picture of where your strengths and weaknesses lie.
In addition to the personality types, the Enneagram includes elements such as the wings, arrows, levels, and subtypes that describe particular traits and how you react to different circumstances. The purpose of these elements is to show how flexible and dynamic your personality can be.
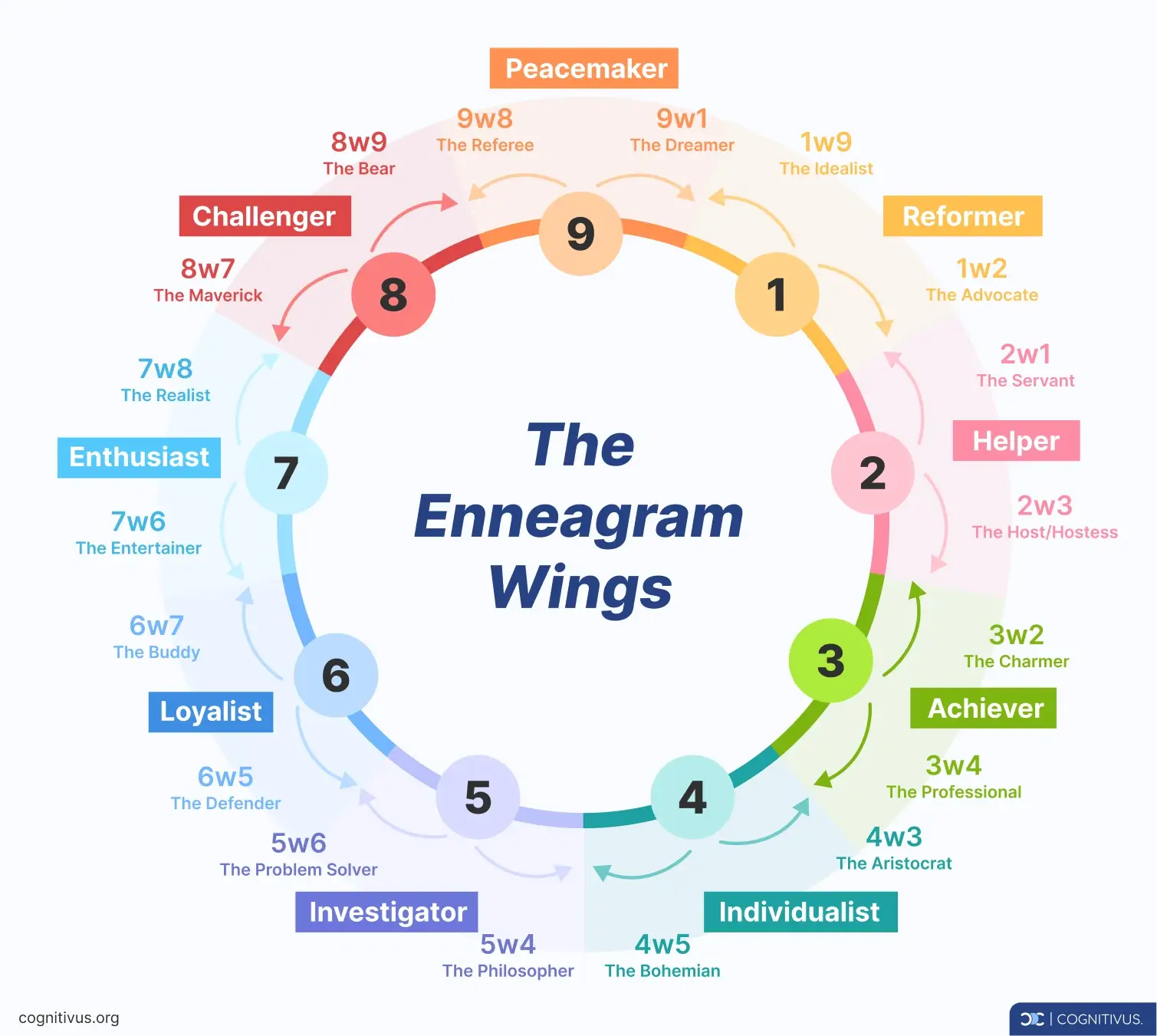
Enneagram wings
The Enneagram wings can be thought of as your influential neighbors. If you're a Type 5, you could lean towards the traits of Type 4 or 6, which represent your wings. This blend provides a more detailed version of your core type.
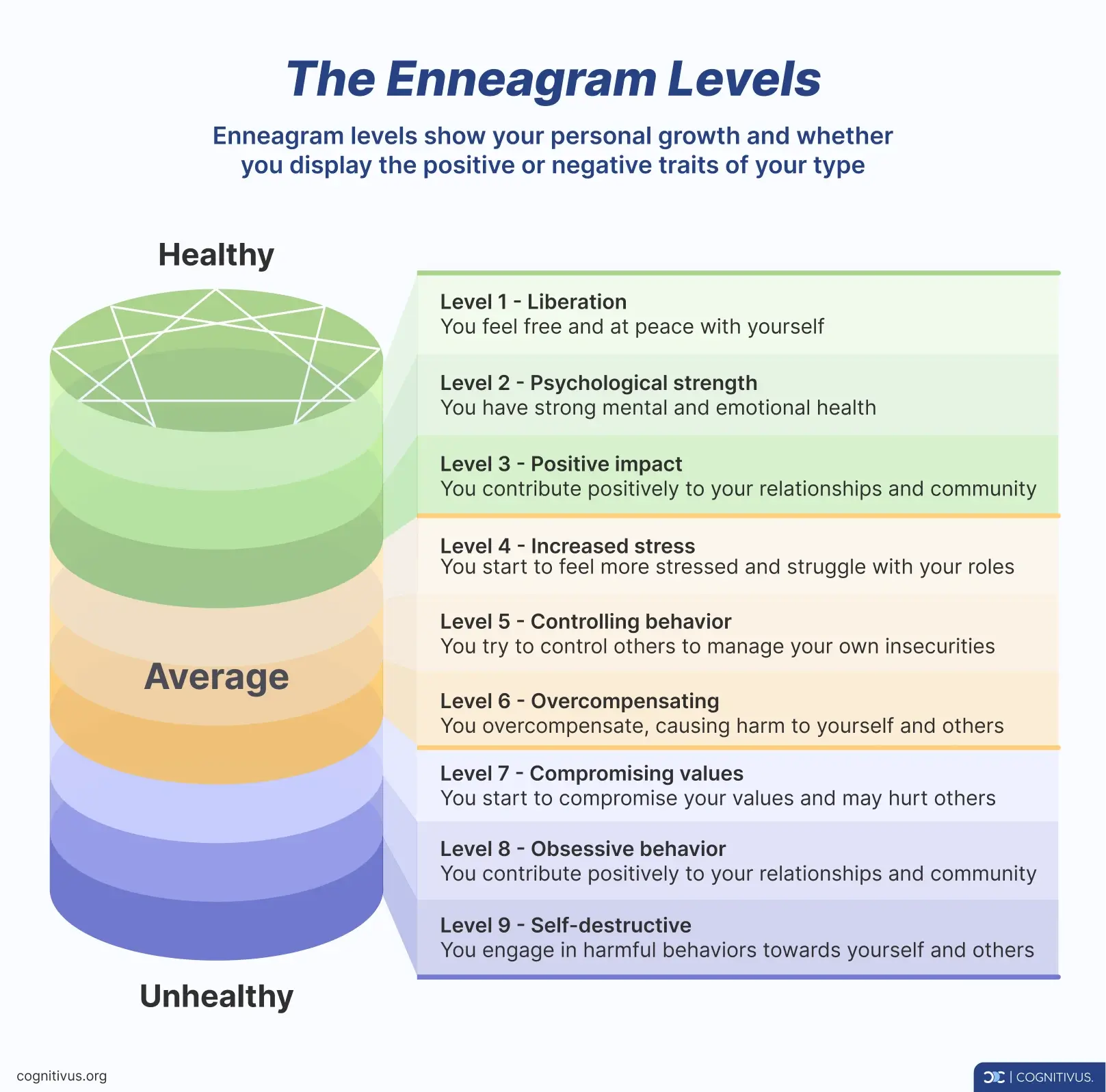
Enneagram levels
Enneagram levels represent stages of growth, like the rungs on a ladder. They show how aligned you are with healthy or challenging aspects of your type. Moving to higher levels of development shows maturity and greater mastery of your strengths.
Enneagram arrows (Lines of stress and growth)
Enneagram arrows point to influences under stress or security, revealing how personality types can change in different situations. The inner lines within the Enneagram symbol connect each type to two other types or traits, revealing how certain personalities can adapt or fall apart under stress.
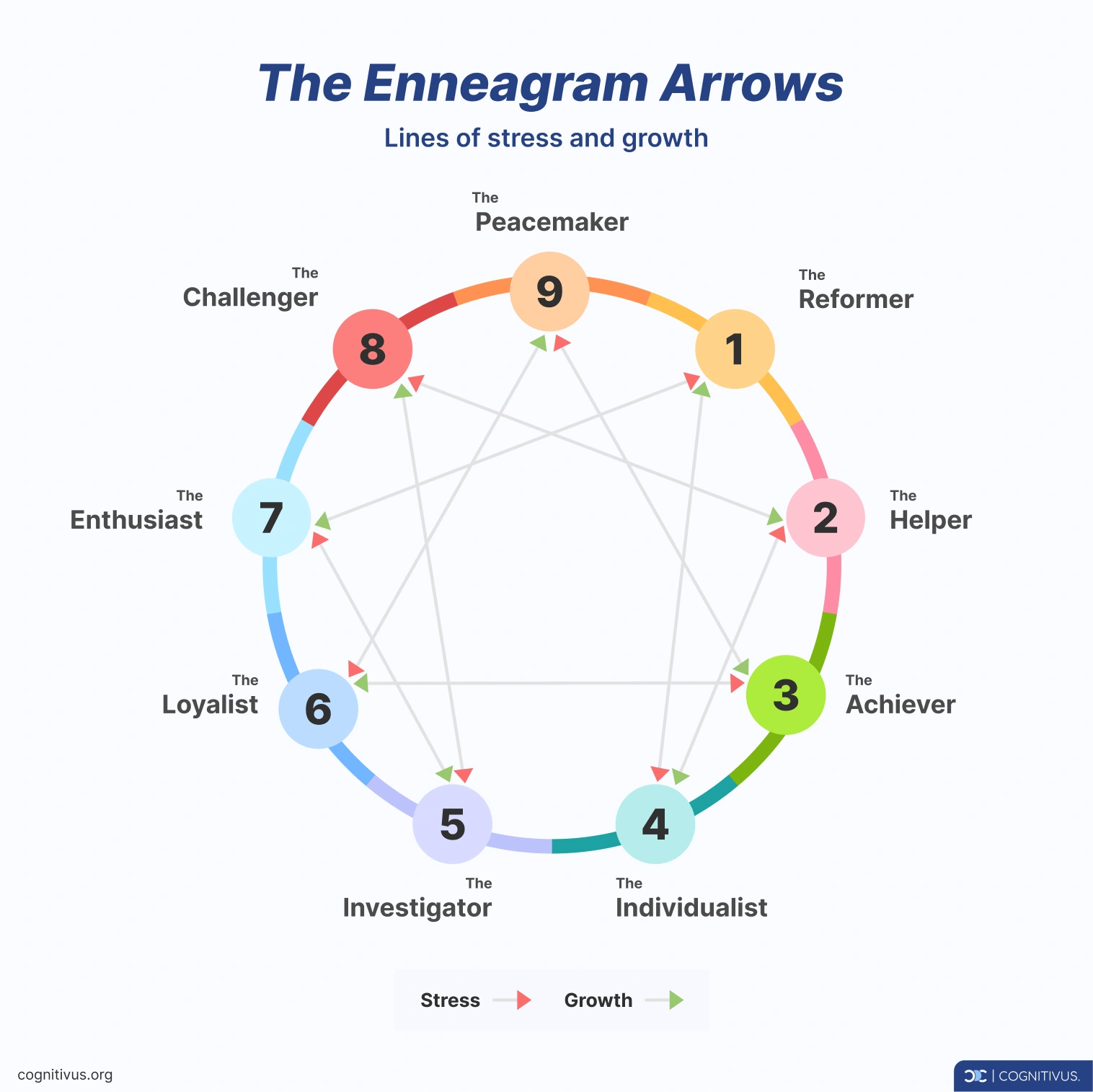
- Lines of stress: This element shows how a specific personality type behaves under pressure. For instance, a Type 5, which is The Investigator, is usually analytical and level-headed, but chronic stress might lead to the unhealthy behaviors of a Type 7, such as distraction and recklessness, in their attempt to escape from reality.
- Lines of growth: The growth lines reveal how a type behaves when they feel secure. If we look at a secure Type 5, they’ll display the strengths of a Type 8, including self-confidence and boldness. They become more decisive and assertive when they’re balanced and fulfilled.
4. The Enneagram Subtypes or Instincts
Apart from our ability to become self-aware and learn what makes us tick, our thoughts and behaviors are also influenced by our instinctual drives. These drives are based on our need for survival on a physical and emotional level.
According to the Enneagram system, there are three instinctual drives that affect our personalities, including: the self-preservation instinct, the sexual (or one-to-one) instinct, and the social instinct.
All three instincts operate at the same time, but one instinct is usually dominant, shaping an individual's attitudes and values.
The self-preservation instinct
This instinct is concerned with survival, well-being, and security. It focuses on health, comfort, food, shelter, routine, and satisfying one’s material needs. People with a dominant self-preservation instinct tend to be disciplined, practically oriented, and goal-focused.
The one-to-one instinct
The sexual (or one-to-one) instinct arises from the primal urge to reproduce and ensure one's genetics continue to the next generation. This subtype involves attraction, courtship, and finding compatibility. Individuals with a dominant sexual instinct seek intense, stimulating relationships and activities.
The social instinct
The social instinct drives social relatedness and intimacy. Those with a dominant Social Instinct need a sense of belonging and strive to connect with others. They are often well-attuned to social hierarchies and may act altruistically to protect and conserve groups for the greater good.
5. The Purpose of the Enneagram
The Enneagram test is your partner in self-discovery. There’s no doubt that it can serve as a catalyst for personal and professional growth. Teams use it to understand each other's positive attributes while friends use it on a social level to deepen their bonds.
Recognizing your Enneagram personality is like discovering a roadmap to your instincts while uncovering your deepest desires. Whether you crave security much like the committed Loyalist (Type 6) or seek freedom such as the enthusiastic Adventurer (Type 7), the Enneagram sheds light on these core motivations.
You only need to look at the behaviors of your colleagues at work to see the Enneagram at play. Perhaps you’ll better understand why the overzealous colleague comes up with outlandish ideas or why the quiet thinker needs time alone to process new information. This personality system goes a long way toward building stronger teams by detailing each member’s strengths.
By learning your Enneagram type, it makes aspects of your behavior and thought patterns much clearer. You can better understand other people, which makes it easier to navigate conflicts with sensitivity, make genuine connections, and thrive rather than exist.
6. How to Choose an Enneagram Test
Are you ready to take an Enneagram test? Here are 10 tips to help you find the right one:
- Credibility: Is the test designed by reputable sources and validated?
Look for tests created by experts or reputable organizations. Validation studies or scientific research can ensure its reliability. - Variety of questions: Does the test offer different types of questions?
Tests should use various question formats, like multiple-choice, pattern recognition, and logical puzzles, to cover different aspects of your personality. - Comprehensive skills assessment: Does the test measure different skills?
A good test should evaluate a range of skills, such as emotional intelligence, creativity, and logical reasoning. This provides a complete picture of your strengths and areas for improvement. - Validity and reliability: Does the test have strong validity and reliability?
According to a study by Kayleigh Kastelein, some Enneagram tests lack reliability and validity. The test you choose must have strong psychometric support to provide accurate results. - Detailed reports: Does the test provide detailed feedback?
Tests should give you detailed reports to help you understand your performance across various traits and offer insights into your personality. - Adaptability: Does the test adjust based on your answers?
Some tests adapt the difficulty of questions based on your responses. Adaptive tests can give a more accurate assessment by tailoring questions to your level. - User reviews: Is the test well-reviewed by users?
Look for tests that others have found insightful and helpful. User reviews can give you a good idea of the test’s accuracy and reliability. - Expert recommendations: Is the test recommended by professionals?
Tests recommended by psychologists or experts in the field are more likely to be reliable. - Cost: Is the test free or paid?
While some free tests can provide useful insights, they aren’t as reliable. Paid tests, especially those developed by experts, tend to offer more accurate and comprehensive assessments. - Honest introspection: are you prepared to answer honestly?
Be ready to answer the questions truthfully. The accuracy of your results depends on how honestly you respond. It's not about passing or failing, but discovering your true self.
7. Which Enneagram Test is the Most Legit?
To help you find the most valid and reliable tests, here’s a list of some of the most popular tests and what you should know about them.
The Riso-Hudson Enneagram Type Indicator (RHETI)
The RHETI test, created by Don Richard Riso and Russ Hudson, is one of the most well-known Enneagram tests. Out of 144 statements on the test, you’ll determine which ones suit you best. Despite its popularity, it has some issues with scientific proof. Psychology expert, Anna Sutton says the RHETI can give consistent results, but it might not always be accurate in identifying your true type.
Wagner Enneagram Personality Style Scales (WEPSS)
Jerome Wagner designed the WEPSS, one of the most detailed Enneagram tests. It uses 200 statements that you rate based on how well they describe you. While detailed, it has limited scientific backing for its accuracy. Sutton points out that different Enneagram tests, like the WEPSS, often give different results.
Integrative Enneagram Questionnaire (IEQ9)
The IEQ9 gives a comprehensive look at your Enneagram type, including subtypes and levels of development. It uses modern methods and provides detailed reports, but lacks scientific proof. The extra details can be interesting, but they also raise questions about their accuracy.
Essential Enneagram Test (EET)
The EET, developed by David Daniels and Virginia Price, involves reading nine paragraphs, each describing one of the Enneagram types, and choosing the one that best matches your personality. This method emphasizes self-reflection and personal insight, making it an introspective process. It is straightforward and engaging, appealing to those who prefer a narrative approach to self-assessment.
So, which Enneagram test should you pick?
With so many different Enneagram tests available, how do you know which one is right for you? Our guidelines make it easier to pick the most compatible and reliable assessment:
- RHETI: If you want a test that is easy to understand and provides consistent results, we recommend the RHETI.
- WEPSS: For a detailed and thorough test, the WEPSS could be a good fit, even though it may not always be scientifically validated.
- IEQ9: For a comprehensive test that includes subtypes and levels of development, consider the IEQ9, but keep in mind its complexity and limited scientific proof.
- EET: If you prefer a straightforward approach that involves self-identification through descriptive paragraphs, the EET might be suitable, though it has moderate reliability and validity.
8. How to Interpret the Enneagram Tests Results
When you first receive your Enneagram test results, you may feel overwhelmed or even confused. But remember that this assessment is meant to help you understand the traits and drives that make you unique.
Each symbol and number represent key aspects of your personality. For example, you might find that you are a Type 2, the Helper, which means you often seek love and appreciation. On the other hand, if you’re a Type 8, the Challenger, your strong decisions shape your everyday behaviors.
The Enneagram test gives you insights from looking inward. Your path of self-discovery will show strengths you didn't know you had or fears you may have overlooked. It can add value to both your personal and professional lives. For example, leaders use it to guide diverse personalities, whereas coaches design training based on your character traits. In your personal life, the Enneagram test allows you to hone in on your emotional intelligence and can help you build more empathetic and understanding relationships.
9. Enneagram Criticism: Can You Trust The Results?
The Enneagram Test makes it possible to peel back the layers of your personality so you can work towards self-improvement across all areas of your life. But despite its relatability, critics often point out its lack of scientific validation.
Compared to the MBTI, which also faces scrutiny but has more scientific backing, the Enneagram does not consistently align with well-established scientific models of personality psychology, like the Big Five personality traits. This is partly because the Enneagram's roots are in ancient wisdom traditions and popular psychology, which contributes to its shaky standing in the scientific community.
Critics also caution against using the Enneagram too rigidly. While it can be a valuable tool for self-discovery, relying on it too strictly can limit personal growth.
So, can I trust the results?
Yes, you can trust the Enneagram test, and that’s because it is a serious tool used in psychology, business, and therapy. In a 2012 paper on the Enneagram, chartered psychologist Anna Sutton points out that while more testing is needed to fully prove its accuracy, the Enneagram still offers valuable insights into how people think and behave. These insights can help you grow personally and improve your relationships. In addition to these insights, the Enneagram community uses reliable research to support their claims rather than mere opinions or trends.
10. Common Enneagram Myths
As with any powerful tool, there are a few myths about the Enneagram personality test that need to be dispelled. Let's clear the air by discussing a few of these myths and what makes this system so valuable.
The Enneagram is a quick fix
The Enneagram shouldn’t be relied on as a test that will make the challenges in your life disappear. It is meant as a stepping stone toward growth, not perfection.
You are just one type
The Enneagram is not only about finding your one true personality type. While you may resonate with a specific type, you must consider all of the traits from the nine personality types and how they influence your behavior.
The Enneagram is similar to a horoscope
Another misconception is that the Enneagram is like a horoscope - unscientific and based only on belief. However, research such as this one published in the European Management Journal, demonstrates the system's potential to improve self-awareness and workplace harmony. The study found that the description of the “whole person” based on unique patterns of traits, values, and motives can aid employee development and talent management.
The Enneagram dictates your future
Nothing is set in stone, and the same applies to the Enneagram. You should use the results to determine where you are, where you can go, and the person you can become.
Use discernment with personality tests
Personality tests such as the Enneagram are meant to inform and guide, not define. Like with all personality tests, you need to use discernment. It's up to you to apply the insights you gain to make the changes you want.
A Final Tip: Celebrate Your Complexity!
The Enneagram is a personality test that encourages you to celebrate your uniqueness, which includes your complexities. By uniting various aspects of your character and personality, you can take charge of your present and future because you’re aware of your shortcomings and strengths.
Not only do you finally have the language to describe how you feel or why you think the way you do, but you also have the motivation to take what you’ve learned and lead a more authentic and fulfilling life.


